
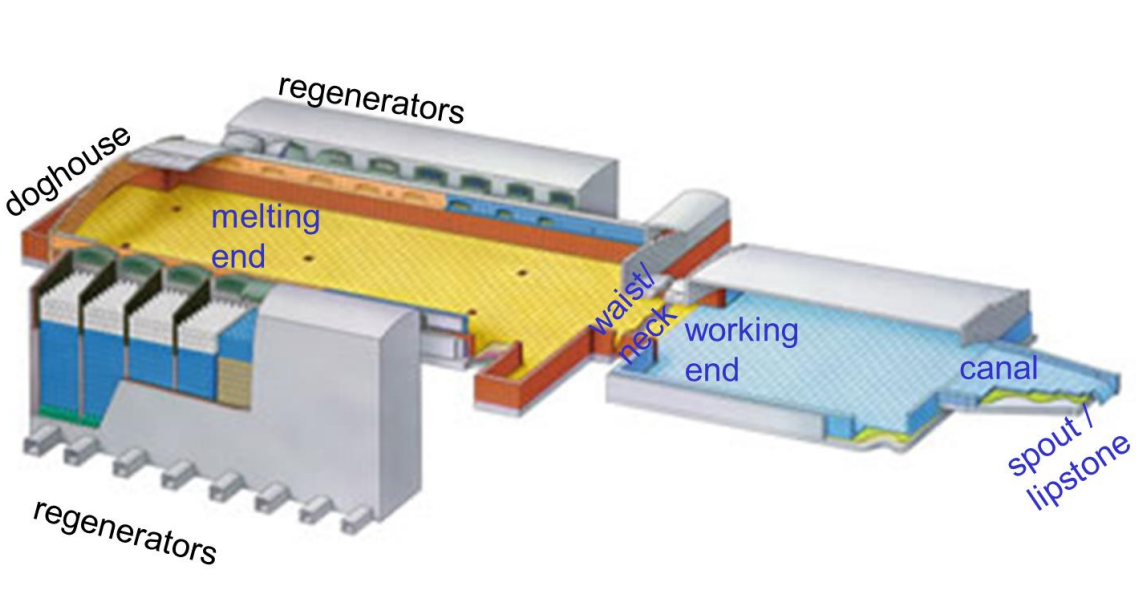
1. Flat Glass Furnace structure:
A flat glass furnace, which is used in the production of flat glass sheets, typically consists of several main parts that work together to melt raw materials and form molten glass. The main parts of a flat glass furnace include:
Melting end (Melter): The Melter is the central part of the furnace where raw materials, such as silica (sand), soda ash, and limestone, are continuously fed into the furnace. The Melter is designed to heat and melt the raw materials, creating a pool of molten glass.
Refiner (Working end): The refiner section of the furnace is responsible for refining the molten glass, removing impurities, bubbles, and other defects. It typically consists of chambers or tanks where the glass is held at a controlled temperature to allow for refining and homogenization.
Forehearth (feeder channel): The forehearth is a channel or passage that connects the melter/refiner section of the furnace to the forming section. It transports the molten glass from the furnace to the forming process. The forehearth helps maintain the desired temperature and consistency of the glass as it flows to the forming equipment.
These are the primary parts of a flat glass furnace, although the specific design and configuration may vary depending on the type of glass being produced, the production method, and other factors.
2. Flat Glass furnace working process
The working process for continuous furnaces is like following:
The batch material enters the melting part from the feeding port, the combustion air enters from one side of the regenerative chamber(regenerator) during combustion, and the flame is ejected from the burner port on one side of the furnace to the other side, and the flame melts the batch materials into glass liquid (molten glass) through heat radiation.
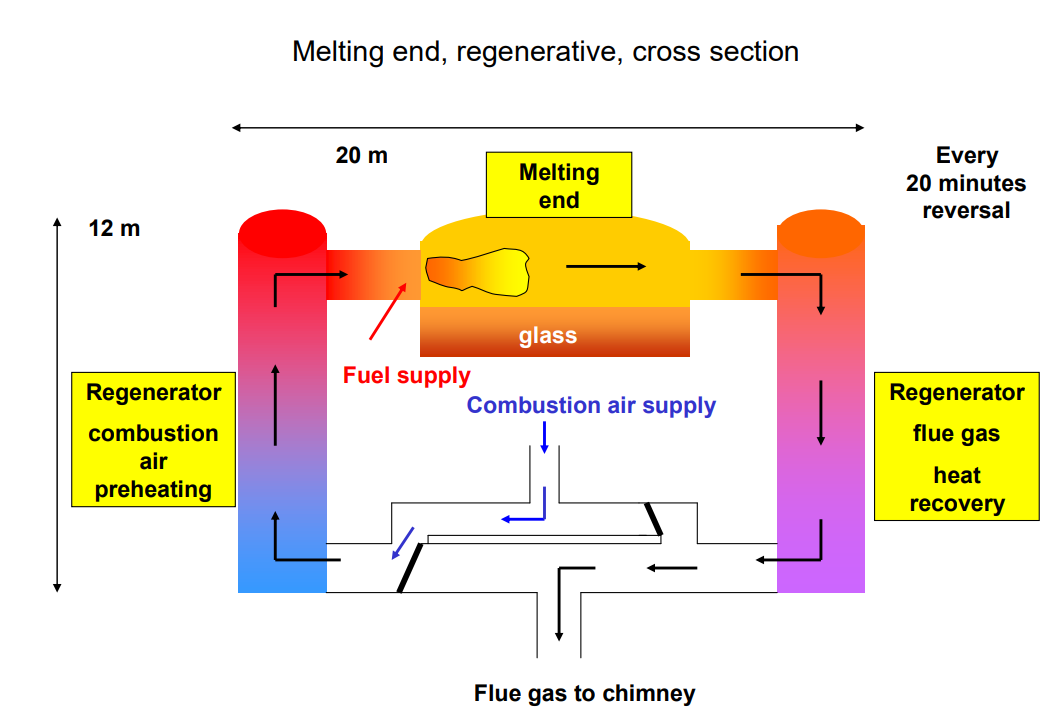
The final exhaust gas enters the regenerator on the other side, and is discharged through the chamber, flue, and chimney. Perform a flame reversal every 20 minutes.
The molten and refined glass liquid enters the cooling part(working end), and after cooling to a certain moulding temperature, it enters the tin bath through the launder.
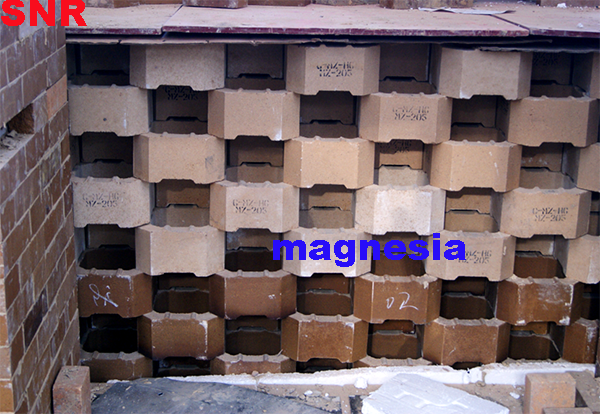
3. Selection of refractory materials
Superstructure (Combustion Area) (Arch, Crown, Refiner superstructure): silica bricks;
Melting Tank: fused zirconia corundum brick (Fuse cast AZS block);
Melting Tank Bottom: corundum brick + zirconium ramming material + clay brick + insulation brick;
Burner: fused zirconia corundum blocks (fuse cast AZS);
Regenerator: silica brick, clay brick, high alumina brick, magnesia block;
Chimney: fireclay brick
L hanging wall: sintered zirconia mullite brick
3.1. Doghouse & L-shape Hanging Wall
Doghouse corner fuse AZS 41, L shape hanging wall fuse cast AZS or sintered zircon mullite bricks.

3.2. Melting Area Crown
Silica brick is applied in crown part.

3.3. Melting End
Fused AZS blocks are applied in melting end sidewall and paving.

3.4 Burner, Melting Sidewall, Melting Tank superstructure
Fuse cast AZS blocks are applied.

3.5. Burner
Fused zircon corundom (AZS Blocks) are applied.

3.6 Melting end superstructure
Fuse cast AZS blocks are used.

3.7 Melting Tank Wall
Fuse cast AZS(fuse cast zirconia corundum blocks) are used.

3.8. Arch (crown)
Silica bricks are used.

3.9. Regenerator
Mainly magnesia blocks are used.

3.10 Regenerative Chamber upper structure
Magnesite checker blocks are applied.

4 Properties and composition of refractories
Refractory materials refer to a class of inorganic non-metallic materials with a refractoriness not lower than 1580°C. Refractoriness refers to the Celsius temperature at which a refractory conical sample can resist high temperature without softening and melting without load.
4.1. Silicon refractories
Materials containing more than 90% SiO2 are usually called siliceous refractory materials, mainly including silica bricks and fused silica products. Silica bricks are produced with silica as the main raw material, and its SiO2 content is generally not less than 93%, and the main mineral composition is phosphoquartz and cristobalite.
The softening temperature of silica brick under load is as high as 1640~1670℃
4.2. Aluminium silicate refractories
4.2.1 Fireclay bricks refer to aluminium silicate refractories with an alumina content of 30% to 48%.
The load softening temperature of clay brick is around 1350℃.
4.2.2 The alumina of high alumina bricks is >48%. Among them, the content of Al2O3 in mullite is 65-75%. Load softening start temperature>1600℃
4.2.3 Corundum brick refers to an aluminium silicate refractory material with an alumina content of more than 95%. Load softening start temperature>1700℃.
4.3. Magnesia refractories
Magnesia refractories refer to alkaline refractories with magnesia as the main raw material, periclase as the main crystal phase, and MgO content greater than 80%.
Magnesia brick load softening start temperature>1550℃
4.4. Zirconium-containing refractories
Zirconium-containing refractory materials refer to refractory materials produced from zirconium-containing materials such as zirconia (ZrO2) and zircon. The main crystal phase of zirconium corundum is α-Al2O3, the secondary crystal phase is baddeleyite, and there is also a small amount of glass phase.
Zirconia corundum brick load softening start temperature>1630℃
Fuse cast zircon corundum blocks, also known as fuse cast AZS blocks, are the main materials applied in glass furnace melting tank, working end, and other part of its structure.
4.5 Mullite bricks
The main component of mullite bricks is Al2O3, and its content is about 75%. Because it is mainly mullite crystals, it is called mullite bricks. The density is 2.7-3.2g/cm3, the open porosity is 1%-12%, and the maximum service temperature is 1500~1700℃. Sintered mullite is mainly used for masonry walls of regenerators.
Fused mullite is mainly used for masonry pool walls, observation holes, wall stacks, etc.
4.6 Fused alumina brick
It mainly refers to fused α, β corundum, and fused β corundum fire-resistant bricks, which are mainly composed of 92%~94% Al2O3 corundum crystal phase, with a density of 2.9~3.05g/cm3.
The porosity is 1%~10%, and the maximum service temperature is about 1700°C.
4.7Quartz brick
The main component of quartz brick is SiO2, which contains more than 99%, the density is 1.9~2g/cm3, the fire resistance is 1650°C, the working temperature is about 1600°C, and it is resistant to acid attack.
It is used to melting tank wall of acid boron silicate glass, the thermocouple hole brick in the combustion area, flame space, etc.
Where can you buy the high-quality refractories blocks?
Zhengzhou SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) is a professional refractory materials manufacturer in China for 30 years. We export refractories to 30 countries for glass factories.
Whatsapp:0086-182 0397 6036,
Email:davis@snrefractory.com.