
What is the process of glass melting and how many types of glass furnace are available recently
The thermal equipment used in glass production is collectively referred to as glass furnaces, including glass melting furnaces, annealing furnaces and some furnaces for glass processing. This article makes everyone understand the glass melting process and the working principle of the glass tank furnace, and then understand the safe, low-consumption and clean production process of glass.
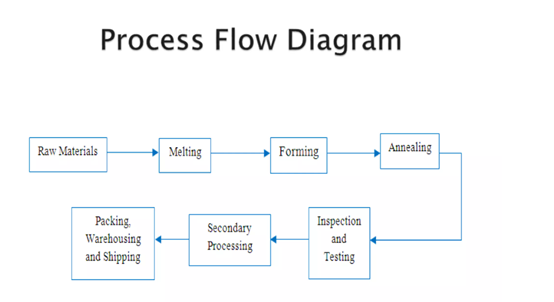
I. What is the process of glass melting?
The melting of glass raw materials is carried out in a glass melting furnace. In order to understand the structure and performance of the glass melting furnace, we must first understand the whole process of glass melting.
1. silicate formation stage
This stage is a series of physical, chemical and physical-chemical changes that occur rapidly under the action of 800~1000°C after the batch enters the furnace, such as heating of powder, evaporation of water, decomposition of salts, polycrystalline transformation, etc.
2. Glass liquid formation stage
When the batch material is heated to 1200°C, various silicates are formed. Until the temperature reaches around 1300°C, the molten glass(liquid) begins to form.
3. Glass liquid Refining stage
After the molten glass formation stage is completed, there are many bubbles and gray bubbles (small bubbles) in the melt. The stage of removing gas inclusions visible to the naked eye and eliminating stomata from the glass liquid is called the clarification stage(Refining). This process is done at high temperatures because the viscosity of the glass decreases rapidly with increasing temperature.
4. Glass liquid homogenization stage
After the glass melt is formed, the chemical composition and temperature of each part of the glass melt are different, and some inhomogeneous bodies are also included, so a homogenization process is required. Its principle mainly relies on diffusion and convection.
5. Glass liquid cooling stage
In order to facilitate the forming of glass, the molten glass should be uniformly cooled to the forming temperature. Generally, the forming temperature is 200~300°C lower than the clarification (refining) temperature.
II. How many types of glass furnaces are there?
Classification of pool furnace
1.According to the heat source
(1) Flame furnace. Combustion of fuel as heat energy source. Fuel can be gas, heavy oil and water.
(2) Electric furnace. Electric energy is used as the heat source.
(3) Flame-electric heating furnace. Fuel is the main heat source, and electric energy is the auxiliary heat source.
2. According to the continuity of the melting process
(1) Batch furnace. The various stages of glass melting are carried out sequentially at the same part of the furnace at different times, and the temperature system of the furnace is variable.
(2) Continuous furnace. The various stages of glass melting are carried out at the same time and in different parts of the furnace, and the temperature system in the furnace is stable.
3. According to the flue gas waste heat recovery equipment
(1) Regenerative furnace. The waste heat of flue gas is recovered by means of heat storage.
(2) Heat exchange furnace. Recover flue gas waste heat by heat exchange.
4. According to the direction of flame flow in the furnace
(1) Horizontal flame furnace. The flame in the furnace flows horizontally, perpendicular to the flow direction of the molten glass.
(2) Horseshoe flame furnace. The flame in the furnace flows in a horseshoe shape.
(3) Vertical flame furnace. The flame in the furnace flows longitudinally, parallel to the flow direction of the glass liquid.
5. According to the products manufactured
(1) Flat glass furnace. Manufacture of flat and rolled glass.
(2) Glass furnaces for daily use. Manufacture bottles, utensils, chemical instruments, electric vacuum glass, etc.
6. According to the size of the furnace
(1) Large furnace. The daily output of molten glass is 150~400t.
(2) Medium-sized furnace. Daily output glass liquid 50~150t.
(3) Small furnace. The daily output of molten glass is below 50t.

III. Main process system and control of glass melting
1. Temperature and Control
One end is the feeding pool(doghouse), the other end is the forming of the product, and the high temperature in the middle is the hot spot. When the material is propelled by the feeder, the pile gradually turns into a foam layer, forming a bubble boundary before the hot spot. Between the bubble boundary and the pile, as the temperature rises, the powdery batch is gradually melted, which is the stage of silicate formation and glass liquid formation. Therefore, a layer of light air bubbles floats on top of the glass liquid.
After passing through the small hot spot furnace, the temperature continues to rise, and after entering the refining and homogenization stage of the glass liquid, the layer of foam disappears, so the bubble boundary is called. The hot spot temperature depends on the composition of the glass and the life of the refractory tank kiln.
In the cooling section, the cooling rate of the molten glass should be slow and steady to prevent secondary air bubbles from being introduced when the temperature rises. The temperature gradient of the cooling section is 7~11°C/m. In order to obtain a reasonable temperature system, a pair of small furnaces(burner) are designed not to fire or to open a small fire.

2. Fuel heating temperature and flame control
The gas heating temperature system has a great influence on glass production. The gas quality is required to be good and stable, and the flame mainly transfers heat in the form of heat radiation, and the brightness of the flame depends on the ratio of fuel properties to air;
The flame length is moderate, if too long, it will burn the opposite furnace wall. If the flame is too short, the coverage area is small, and the temperature distribution is uneven.

VI. Main structure of Flame glass furnace
1. glass melting part
(1) Melting part. It is the part that melts the batch material and refines and homogenizes the molten glass. The upper part of the melting part is the flame space, and the lower part is the furnace pool(furnace tank). The flame is mainly ejected from the combustion port of the small furnace(burner).
(2) Feeding port. The batch material is put into the furnace from the feeding port, and the heat is transferred by the flame space and the glass liquid.
(3) Cooling section. It is the part where the molten glass is further homogenized and cooled, and it is also the channel for distributing and feeding the molten glass.
2. Heat source supply part
(1) Air and gas channels. It is the channel through which the heated air and gas flow before entering the pre-combustion chamber after leaving the regenerator. It is also the channel through which the flue gas is discharged from the flame space to the regenerator.
(2) Pre-chamber. After the air and gas leave the horizontal channel, they are partially mixed before entering the furnace with the help of airflow vortex, molecular diffusion and mutual impact.
(3) Flare vents. Refers to the place where flames spew out. The shape, size and length of the vent have a great influence on the speed, thickness, width and direction of the flame. Oil burners are simpler and only use nozzles.
3.Waste heat recovery part
In order to increase the flame temperature in the furnace, a flue gas waste heat recovery device is installed to use the waste heat of the flue gas to heat the combustion-supporting air and flue gas, thereby achieving the effect of increasing the flame temperature and saving energy.
4.Air supply and exhaust discharge part
In order to ensure the continuous, normal and effective operation of the tank furnace, a set of exhaust gas supply system is set up. Including exchanger, air, flue gas, intermediate flue, blower, main flue and chimney.

Where can you buy the high-quality refractory bricks?
Zhengzhou SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) is a professional refractory materials manufacturer in China for 30 years. We export refractories to 30 countries for glass factories.
Whatsapp:0086-182 0397 6036,
Email:davis@snrefractory.com.