
Glass furnaces are the core equipment in glass production, and their operating conditions directly affect the quality and production efficiency of glass products. Fused cast AZS blocks, as the key refractory materials in glass furnaces, undertake important tasks such as withstanding high temperatures and resisting erosion. The quality of these blocks directly influences the service life of the glass furnace and the stability of production. Therefore, establishing scientific and reasonable quality confirmation principles for fused cast AZS blocks is of utmost importance. This article will focus on this topic and conduct an in-depth discussion on the quality confirmation principles for fused cast AZS blocks used in glass furnaces.

1. Basic Performance Compliance Principle
1.1 High Temperature Resistance
Glass furnaces are the core equipment in glass production, and the interior of the furnaces creates an extremely demanding high-temperature environment. From the overall structure of the furnace, different parts bear different levels of high-temperature strength due to functional differences and the distribution of flames, as well as the flow of the glass liquid. For example, the fused cast AZS blocks near the flame spraying area are directly exposed to the scorching heat of the high-temperature flames, and the degree of high temperature they face is much higher than other parts; while the fused cast AZS blocks located near the glass liquid flow channel have to endure the continuous high temperature transferred by the glass liquid for a long time.
High-quality fused cast AZS blocks must possess the outstanding ability to work stably in the corresponding high-temperature environment. Under the continuous effect of high temperature, the fused cast AZS blocks must not undergo softening. Once softening occurs, the original shape and structure of the bricks will be damaged, unable to provide stable support and sealing functions for the furnace, thereby affecting the normal flow and reaction process of the glass liquid within the furnace. At the same time, they must not deform; even a slight deformation can cause the furnace's masonry structure to loosen, leading to material leakage, air leakage, and other problems, not only causing waste of raw materials but also reducing the thermal efficiency of the furnace and increasing energy consumption. They must not melt either. Melting means that the fused cast AZS blocks have lost their basic function as refractory materials, directly causing damage to the local structure of the furnace, and in severe cases, even triggering furnace shutdown for maintenance, resulting in huge economic losses for the glass manufacturing enterprise.
1.2 Resistance to Erosion
During the operation of the glass furnace, the molten glass exhibits strong erosion on the fused cast AZS blocks. This erosion becomes more significant under high-temperature conditions. The molten glass is typically composed of various chemical components, such as silicon dioxide, sodium oxide, and calcium oxide. These components have high chemical reactivity at high temperatures and can undergo chemical reactions with the substances in the fused cast AZS blocks, thereby causing erosion of the bricks.
High-quality fused cast AZS blocks should have excellent resistance to erosion, which is crucial for ensuring their long-term use in the glass furnace. Fused cast AZS blocks with good resistance to erosion can effectively resist the erosion of various chemical components in the molten glass during contact, like a sturdy protective shield, preventing chemical substances from reacting with the internal structure of the bricks, thereby reducing the loss and deterioration of the brick. If the resistance to erosion of the fused cast AZS blocks is poor, the surface of the bricks will gradually be eroded under the long-term erosion of the high-temperature molten glass, resulting in a thinner brick body and reduced strength. As the erosion intensifies further, the internal structure of the brick will also be damaged, showing signs of looseness, cracking, etc., ultimately making the fused cast AZS blocks lose their usability.
Only fused cast AZS blocks with resistance to erosion meeting the specified standards can ensure long-term use in the glass furnace without serious damage. Such fused cast AZS blocks can provide lasting protection for the furnace, reducing the frequency of furnace maintenance and replacement due to damage to the fused cast AZS blocks, thereby extending the service life of the furnace and reducing the cost of glass production.
1.3 Thermal Shock Stability
During the operation of a glass furnace, the temperature is in a dynamic state and undergoes frequent changes. For instance, during the opening of the furnace, it is necessary to rapidly heat the furnace from room temperature to the working temperature required for glass production; while during the shutdown of the furnace, it is necessary to gradually cool the high-temperature furnace to room temperature. Additionally, during the production process, due to factors such as flame adjustment and the flow of the glass liquid, local temperature fluctuations may occur within the furnace. Such rapid temperature changes impose extremely high requirements on the thermal shock stability of fused cast AZS blocks.
Fused cast AZS blocks must possess excellent thermal shock stability, meaning they should not exhibit cracks, peeling, or other defects when subjected to rapid temperature changes. When fused cast AZS blocks are rapidly heated or cooled, thermal stress will be generated within the brick. If the thermal stress exceeds the strength limit of the brick, cracks will occur. The appearance of cracks not only reduces the strength and sealing performance of the fused cast AZS block but also provides a penetration channel for the glass liquid and external air, accelerating the erosion and damage of the fused cast AZS block. As the cracks expand and increase, the fused cast AZS block may experience peeling, further damaging the structural integrity of the furnace.
2. Principle of Accuracy in Appearance and Dimensions
2.1 Appearance Quality
The appearance quality of fused cast AZS blocks holds an important position in the entire glass furnace system. It directly and significantly affects the installation process of fused cast AZS blocks and their subsequent usage effects. In the construction and installation of glass furnaces, flat and smooth fused cast AZS blocks can be more closely adhered together, ensuring the stability and sealing of the construction structure. If the surface of the fused cast AZS blocks is uneven, cracks will appear during the construction, which not only cannot guarantee the overall strength of the furnace but also may lay the groundwork for potential safety hazards such as glass liquid leakage and gas escape.
Qualified fused cast AZS blocks should present a smooth and flat ideal surface, without obvious cracks, pores, inclusions, etc. Cracks are like "time bombs" inside the fused cast AZS blocks; their presence will greatly reduce the strength of the fused cast AZS blocks. In the harsh working environment of high temperature and high pressure of the glass furnace, cracks will become stress concentration areas, and as the furnace operates, cracks will continuously expand and extend, eventually causing the fused cast AZS blocks to break and deteriorate. Moreover, cracks will damage the integrity of the fused cast AZS blocks, providing an erosion channel for the chemical components in the glass liquid, accelerating the decline in the anti-erosion performance of the fused cast AZS blocks, and shortening their service life.
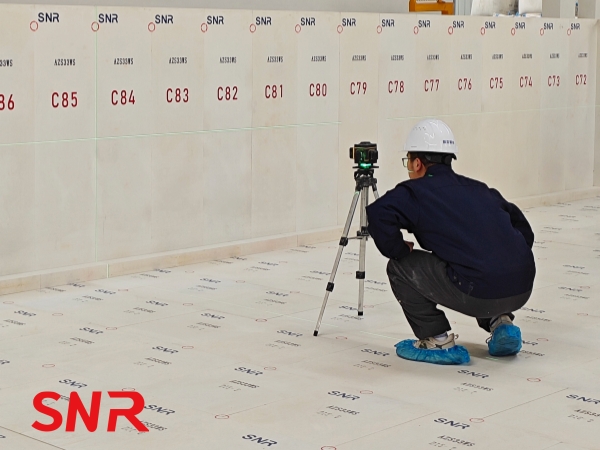


Air holes and inclusions are also harmful factors to the quality of fused cast AZS blocks. Air holes are cavities formed in the production process of fused cast AZS blocks due to incomplete gas expulsion. These cavities weaken the density of the fused cast AZS blocks and reduce their physical properties. Under the erosion of the glass liquid, air holes will become erosion breakthroughs, and the glass liquid will penetrate the interior of the fused cast AZS blocks along the air holes, accelerating the damage of the brick. Inclusions refer to substances mixed into the fused cast AZS blocks that are not part of their own composition, such as impurity particles. Inclusions will disrupt the chemical uniformity of the fused cast AZS blocks, causing differences in the anti-erosion performance and strength of local areas compared to other parts. Under the erosion and thermal stress of the glass liquid, these weak areas are prone to cracks and damage.
When inspecting the quality of fused cast AZS blocks, visual examination is an essential step. It is the most fundamental and widely used method, requiring experienced inspectors to carefully check the surface under adequate lighting from various angles for obvious defects such as cracks, pores, and inclusions. However, visual inspection has limitations and may miss subtle flaws. Therefore, it should be supplemented with non-destructive testing (NDT) methods. For instance, ultrasonic testing uses sound wave reflection and refraction to detect internal cracks and voids, while X-ray testing reveals hidden inclusions by capturing variations in material density. Combining visual and NDT techniques enables a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the appearance quality of fused cast AZS blocks, ensuring compliance with requirements.
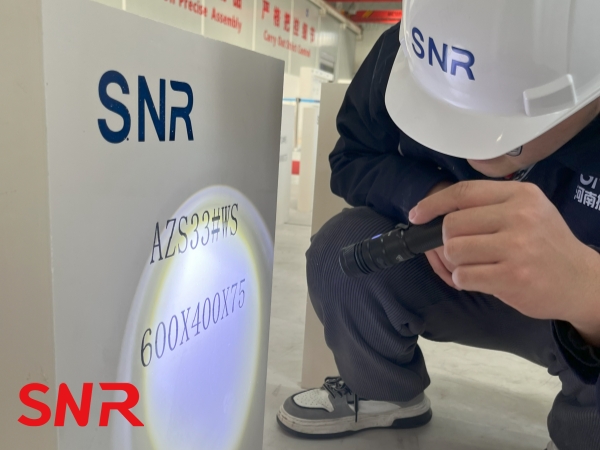

2.2 Dimensional Accuracy
Glass furnace construction requires extremely high precision. As the basic unit of construction, the dimensional accuracy of fused cast AZS blocks is directly related to the quality of construction and overall performance of the furnace.
If the dimensions of the fused cast AZS blocks are inaccurate, the gaps formed after construction will not be effectively sealed, which will lead to problems such as material leakage and gas leakage during the operation of the furnace. Material leakage not only causes waste of raw materials and increases production costs, but also may damage the surrounding equipment of the furnace; gas leakage will affect the temperature and pressure control in the furnace, resulting in temperature fluctuations during the glass production process, and affecting the quality and uniformity of the glass. In addition, gas leakage will increase the heat loss of the furnace, reduce energy utilization efficiency, and increase energy consumption.
Therefore, during the quality confirmation process, precise measuring tools must be used to strictly measure the dimensions of the electrically fused bricks. Common measuring tools include vernier calipers, micrometers, right-angle rulers, etc. These tools have high measurement accuracy and can accurately measure the basic dimensions, such as the length, width, and height of the fused cast AZS blocks. During the measurement, the specified measurement methods and measurement parts should be followed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results. At the same time, according to the design requirements of the glass furnace and relevant standards, the allowable deviation range of the fused cast AZS block dimensions should be determined, and the measured dimension data should be compared with the allowable deviation range to ensure that the dimension deviation of the fused cast AZS blocks is within the allowable range.
For some special-shaped fused cast AZS blocks, such as arc-shaped bricks and irregular-shaped bricks, in addition to detecting the basic dimensions such as length, width, and height, their geometric parameters, such as angle and curvature, should also be detected. These special-shaped fused cast AZS blocks usually play a key role in the glass furnace, and the accuracy of their angles and curvatures directly affects the structural shape and performance of the furnace. For example, inaccurate curvature of the arc-shaped brick will cause the inner wall of the furnace to be uneven, affecting the flow and shaping of the glass liquid; deviation in the angle of the irregular-shaped brick may prevent the bricks from closely fitting each other, reducing the sealing performance of the furnace. Therefore, when detecting special-shaped fused cast AZS blocks, specialized measuring tools and methods such as angle rulers and curvature gauges should be used to ensure that their geometric parameters meet the design requirements, thereby ensuring the overall quality and performance of the glass furnace.
3. Principle of Process Standardization
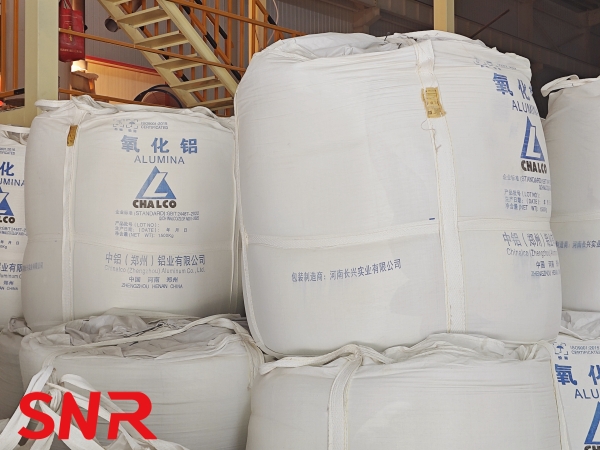
3.1 Quality Control of Raw Materials
The quality of fused cast AZS blocks largely depends on the quality of raw materials. High-quality raw materials are the foundation for producing high-quality fused cast AZS blocks. During the quality confirmation process, strict inspections of the raw materials used in the production of fused cast AZS blocks are necessary, including chemical composition and physical properties indicators. Ensuring the stability and reliability of raw material quality and compliance with production process requirements is crucial. At the same time, attention should be paid to the source and supply stability of raw materials to avoid fluctuations in the quality of fused cast AZS blocks due to raw material quality issues.

3.2 Execution of Production Process
A standardized production process is the key to ensuring the quality of fused bricks. During the production process, operations should be carried out strictly in accordance with the established process parameters, such as melting temperature, melting time, forming pressure, etc. Any deviation in process parameters may affect the performance and quality of fused cast AZS blocks. Therefore, during the quality confirmation, the execution of the production process should be inspected, checking production records, operation procedures, etc., to ensure that the production process complies with the process requirements. At the same time, the operation status of production equipment should be monitored, and equipment maintenance and repair should be carried out regularly to ensure the normal operation of equipment, providing a guarantee for the production of high-quality fused cast AZS blocks.
4. Principle of Supplier Qualification and Reputation
4.1 Supplier Qualification
Selecting suppliers with good qualifications is an important prerequisite for ensuring the quality of fused cast AZS blocks. Qualified suppliers should have relevant production licenses, quality management system certifications, etc. These certificates are important proof that suppliers have the ability to produce qualified fused cast AZS blocks and guarantee the quality. During the quality confirmation process, strict reviews of supplier qualifications should be conducted to ensure their legal and compliant operation. At the same time, attention should be paid to the production scale and technical strength of suppliers, choosing those with a certain scale and technical level to ensure they can provide stable, high-quality fused cast AZS block products.
4.2 Supplier Reputation
Supplier reputation is also an important factor to be considered in the quality confirmation process. A good reputation means that suppliers can strictly fulfill contracts, provide products on time, in quality, and in quantity, and have good after-sales services. Historical transaction records and customer evaluations of suppliers can be consulted to understand their reputation status. Choosing reputable suppliers can reduce procurement risks and ensure the quality and stability of the supply of fused cast AZS blocks.
5. Conclusion
The quality confirmation of fused cast AZS blocks for glass furnaces is a systematic and complex process that requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors. Meeting the basic performance requirements is the core of the quality of fused cast AZS blocks. Precise appearance and size are the basis for ensuring the quality of furnace lining construction. Standardization of the production process is the key to ensuring the stability of the quality of fused cast AZS blocks. Supplier qualification and reputation are important links to ensure the quality of fused cast AZS blocks from the source. Only by following these quality confirmation principles and strictly controlling the quality of fused cast AZS blocks can reliable guarantees be provided for the efficient and stable operation of glass furnaces, and improve the quality and efficiency of glass production.
Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) focuses on producing high-quality refractory materials. If you have any needs, please contact me.
 WhatsApp:+86 188 3808 9557
WhatsApp:+86 188 3808 9557
Email:moon@snrefractory.com