
Glass furnaces are the key equipment in the glass production process, their internal environment is bad, and high temperature, strong corrosive media, and other factors will cause serious erosion of the furnace lining material. As a commonly used high-quality refractory material, fused cast AZS block has the advantages of high melting point and strength. Still, it will inevitably be eroded during the long-term operation of a glass furnace. It is of great significance for optimizing furnace design, selecting refractories reasonably, and taking effective maintenance measures to understand the erosion characteristics of fused cast AZS block in glass furnaces.
1.Basic characteristics of fused cast AZS block
2.The appearance of erosion
3.Microstructure characteristics of erosion
4.Influence on fused cast AZS block properties
5.Analysis of the causes of erosion
6.Measures to deal with the erosion of fused cast AZS block
1.Basic characteristics of fused cast AZS block
Fused cast AZS blocks are usually made by melting high-purity raw materials at high temperatures in electric arc furnaces and then cooling them. Its main components include alumina, zirconia, etc., with dense crystal structure and good high temperature resistance, it can withstand the high temperature environment in the glass furnace, and resist the erosion of the glass liquid and the furnace atmosphere to a certain extent, so it is widely used in the key parts of the glass furnace.

a. Surface melting damage. Under the high temperature of the glass furnace, the surface of the fused cast AZS block in contact with the glass liquid will gradually melt damage. The surface becomes rough and uneven, and the otherwise smooth 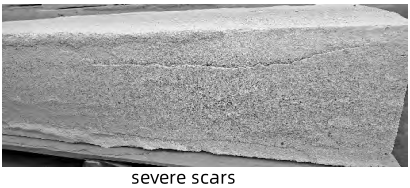 block surface appears dents and potholes. Over time, these melting areas will continue to expand and deepen, which will lead to thinning of block thickness and affect the structural stability of the furnace. For example, in areas where the glass liquid flow is more intense, such as the part of the sidewall near the inlet and outlet of the glass liquid, the degree of melting damage on the surface of the fused cast AZS block is often more obvious, and sometimes there are obvious gully wear marks, which is due to the erosion of the glass liquid to accelerate the melting and loss of the surface material.
block surface appears dents and potholes. Over time, these melting areas will continue to expand and deepen, which will lead to thinning of block thickness and affect the structural stability of the furnace. For example, in areas where the glass liquid flow is more intense, such as the part of the sidewall near the inlet and outlet of the glass liquid, the degree of melting damage on the surface of the fused cast AZS block is often more obvious, and sometimes there are obvious gully wear marks, which is due to the erosion of the glass liquid to accelerate the melting and loss of the surface material.
b. Color change. The surface color of the eroded fused cast AZS block will change. Under normal circumstances, the color of the uneroded fused cast AZS block is uniform, but after being eroded by impurities in the glass liquid, the surface of the block will appear dark spots or color. This is because chemical reactions occur during the erosion process, creating new compounds that deposit on the surface of the block or change the optical properties of the original crystal, resulting in color changes. For example, when impurities such as iron ions in the glass liquid react with some components in the fused cast AZS block, it may make the surface of the block appear brown or black spots, and these color changes can be used as an intuitive reference indicator of the degree of erosion of the fused cast AZS block.
c. Crack generation. Under high temperature and erosion environments for a long time, thermal and chemical stresses will occur inside the fused cast AZS block, and the accumulation of these stresses may lead to cracks on the surface or even inside the block. The cracks may initially be small hairline cracks, and with the intensification of erosion and the continuous action of stress, the cracks will gradually expand and increase, forming a network or larger penetrating cracks. In the temperature fluctuation area of the furnace, such as the junction of the crown and the sidewall, because the temperature changes are more frequent, the fused cast AZS block is more prone to crack due to thermal stress. These cracks will not only reduce the strength of the block but also provide a channel for further penetration of the erosion medium and accelerate the damage of the block.
of stress, the cracks will gradually expand and increase, forming a network or larger penetrating cracks. In the temperature fluctuation area of the furnace, such as the junction of the crown and the sidewall, because the temperature changes are more frequent, the fused cast AZS block is more prone to crack due to thermal stress. These cracks will not only reduce the strength of the block but also provide a channel for further penetration of the erosion medium and accelerate the damage of the block.
3.Microstructure characteristics of erosion
(1) Crystal structure damage. Through microscope observation, it can be found that the crystal structure of the eroded fused cast AZS block is damaged. Crystal lattice defects, dislocations and other phenomena occur in the regular arrangement of the crystal, and the crystal boundary becomes blurred. Under the action of glass erosion, some crystals dissolve, which leads to the weakening of the bond between crystals. For example, after the alumina crystal in the fused cast AZS block reacts with the alkaline component in the glass liquid, part of the alumina will dissolve into the glass liquid in the form of ions, making the integrity of the crystal damaged, which will directly affect the strength and corrosion resistance of the block, making it more vulnerable to further erosion.
(2) Increased porosity .During the erosion process, new pores or the size and number of original pores will be increased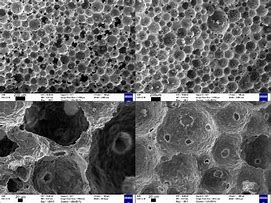 inside the fused cast AZS block. This is caused by the gas produced by the chemical reaction and the evaporation of the glass liquid after penetrating into the interior of the block body at high temperatures. The increase of porosity will reduce the density of the block, making it easier for the erosion medium to spread into the interior of the block, thus accelerating the erosion process. Moreover, the existence of pores will also reduce the thermal conductivity of the block, affect the thermal performance of the furnace, resulting in uneven heat distribution in the furnace, and further affect the melting quality and production efficiency of the glass.
inside the fused cast AZS block. This is caused by the gas produced by the chemical reaction and the evaporation of the glass liquid after penetrating into the interior of the block body at high temperatures. The increase of porosity will reduce the density of the block, making it easier for the erosion medium to spread into the interior of the block, thus accelerating the erosion process. Moreover, the existence of pores will also reduce the thermal conductivity of the block, affect the thermal performance of the furnace, resulting in uneven heat distribution in the furnace, and further affect the melting quality and production efficiency of the glass.
(3) Element diffusion and chemical reaction layer formation. At the interface between the fused cast AZS block and the glass liquid, the element diffusion phenomenon will occur. The alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, and other elements in the glass liquid will spread to the interior of the block body, and some elements in the block body will also dissolve into the glass liquid. The exchange and diffusion of this element will form a chemical reaction layer at the interface, the chemical composition and physical properties of the layer are different from the original block and glass liquid. The thickness of the chemical reaction layer will gradually increase with the increase of erosion time, and its hardness, density, and other properties will also change, generally becoming looser and easier to be washed away by the glass liquid, so that the erosion of the fused cast AZS block continues to push inward.
4.Influence on fused cast AZS block properties
►Strength reduction
The strength of fused cast AZS blocks decreases significantly due to erosion characteristics such as surface melting, crack generation, and crystal structure damage. During the long-term operation of the furnace, the block body may not be able to withstand its gravity and the pressure and scouring force of the glass liquid, resulting in safety hazards such as the block falling off and collapsing, which seriously affects the normal operation of the furnace. For example, after the strength of the fused cast AZS block on the sidewall is reduced, there may be local block drop, so that the glass liquid leaks into the thermal insulation layer or the basic structure of the furnace, which will not only cause the interruption of glass production, but also may damage other parts of the furnace, bringing huge economic losses.
►Thermal conductivity changes
As mentioned above, the increase of porosity and the change of crystal structure caused by erosion will change the thermal conductivity of the fused cast AZS block. In general, the thermal conductivity will be reduced, which will affect the heat transfer efficiency in the furnace. In the glass melting process, the heat can not be transferred to the glass liquid in a timely and uniform manner, which will lead to the uneven melting of the glass liquid, and the phenomenon of local overheating or undercooling, affecting the quality and output of the glass. At the same time, in order to maintain the temperature in the furnace, more energy needs to be consumed, increasing the production cost.
►Erosion resistance is further reduced
 With the development of erosion, the corrosion resistance of fused cast AZS blocks will continue to decline, forming a vicious circle. The erosion of the surface makes the block more vulnerable to the subsequent attack of glass liquid and corrosive medium, and the destruction of the internal structure weakens the overall performance of the block, making the erosion speed gradually accelerate. In the later operation stage of the glass furnace, it may be necessary to frequently repair or replace the furnace lining, which not only increases the workload and cost of equipment maintenance but also affects the continuity and stability of glass production.
With the development of erosion, the corrosion resistance of fused cast AZS blocks will continue to decline, forming a vicious circle. The erosion of the surface makes the block more vulnerable to the subsequent attack of glass liquid and corrosive medium, and the destruction of the internal structure weakens the overall performance of the block, making the erosion speed gradually accelerate. In the later operation stage of the glass furnace, it may be necessary to frequently repair or replace the furnace lining, which not only increases the workload and cost of equipment maintenance but also affects the continuity and stability of glass production.
5.Analysis of the causes of erosion
►The influence of the composition of glass liquid
The alkali metal oxides in the glass liquid (such as Na2O, K2O) and other components are highly corrosive, and they will react chemically with aluminum oxide and silicon oxide in the fused cast AZS block at high temperatures to form low-melting compounds, which are easily taken away under the wash of the glass liquid, resulting in the erosion of the block body. In addition, the impurity content in the glass liquid and the type of glass (such as sodium-calcium glass, borosilicate glass, etc.) are different, and the erosion degree of the fused cast AZS block is also different. For example, the boron element in the borosilicate glass liquid will undergo special chemical reactions with certain components in the fused cast AZS block, accelerating the erosion process.

►Temperature factor
The high-temperature environment in the glass furnace is one of the important factors for the erosion of fused cast AZS block. The high temperature will accelerate the rate of chemical reaction, making the erosion reaction between the glass liquid and the block more intense. At the same time, there will inevitably be temperature fluctuations during the operation of the furnace, such as feeding, discharging, and heating and cooling stages of the furnace, etc., the rapid temperature change will lead to thermal stress inside the block body, which will be superposition with the erosion effect, which will aggravate the damage of the block body. For example, during the heating process of the furnace, if the heating rate is too fast, the fused cast AZS block may crack due to excessive thermal stress, which provides an intrusion channel for the erosion medium and accelerates the occurrence of erosion.
►The role of furnace atmosphere
The atmosphere in the furnace (such as oxidation atmosphere, and reduction atmosphere) will also have an impact on the erosion of the fused cast AZS block. In an oxidizing atmosphere, some metal elements in the fused cast AZS block may be oxidized to form an oxide layer, which has a different nature from the original block and may affect the corrosion resistance of the block. In a reducing atmosphere, some oxides may be reduced, resulting in changes in the structure and composition of the block, which will also reduce its ability to resist erosion. For example, in a furnace atmosphere containing a certain sulfur content, sulfur will react with certain components in the fused cast AZS block to produce sulfide, which has a low melting point and is easily washed away by the glass liquid, accelerating the erosion of the block.
6.Measures to deal with the erosion of fused cast AZS block
Optimize furnace design
In the furnace design stage, the use position and structural form of the fused cast AZS block should be reasonably planned to minimize the erosion and erosion of the glass liquid. For example, optimize the shape and angle of the sidewall to make the flow of glass liquid more stable and reduce the impact force on the sidewall block; Use a thickened or special structure of fused cast AZS block in vulnerable parts to improve its corrosion resistance. At the same time, the thermal insulation structure of the furnace is reasonably designed to reduce the influence of temperature fluctuations on the thermal stress of the fusing block, and through accurate thermal calculation, the temperature distribution in the furnace is uniform and the erosion caused by local overheating or undercooling is reduced.
Choose the right material for the fused cast AZS block
According to the specific working conditions of the glass furnace (such as glass liquid composition, temperature, furnace atmosphere, etc.), the fused cast AZS block with targeted corrosion resistance is selected. For example, for glass liquid with high alkali content, fused cast AZS blocks with high purity, high aluminum content, and appropriate alkali-resistant ingredients (such as zircalite, etc.) can be selected to improve their resistance to alkali metal oxides; In the area of high temperature and large temperature fluctuation, the varieties of fused cast AZS blocks with good thermal stability can be selected to reduce the damage of thermal stress to the block body. In addition, it is also possible to consider the use of new fused cast AZS block materials, such as by adding special additives or using advanced preparation processes, to further improve the comprehensive performance of fused cast AZS blocks and extend their service life in the furnace.


Control furnace operation parameters
During the operation of the glass furnace, parameters such as temperature and atmosphere are strictly controlled. Maintain a stable furnace temperature, avoid large temperature fluctuations, operate according to a reasonable heating and cooling curve, and reduce the damage of thermal stress to the electric melting block. At the same time, the atmosphere composition and pressure in the furnace are precisely controlled, and the atmosphere is adjusted to the appropriate state according to the requirements of the glass production process, and the erosion reaction of the fused cast AZS block caused by the atmosphere factor is suppressed.
Regular maintenance and testing
Establish regular furnace maintenance and inspection system, timely detect the erosion of fused cast AZS blocks, and take corresponding measures. Regular inspection of the furnace lining, including appearance inspection and non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic detection, thermal imaging detection, etc.), through the appearance observation can be found in time the melting, cracks, color changes, and other erosion characteristics of the surface of the fused cast AZS block, and non-destructive testing can more accurately understand the structural changes and damage degree inside the block. According to the test results, the parts with light erosion should be repaired, such as local repair with hot repair materials; For areas with serious erosion, timely replacement of damaged fused cast AZS blocks to avoid local damage resulting in a decline in the overall performance of the furnace and the occurrence of safety accidents.
The erosion of fused cast AZS block in a glass furnace is a complicated process, and its characteristics are obvious in appearance, microstructure, and block properties. Erosion results from many factors such as the composition of glass liquid, temperature, and furnace atmosphere. By optimizing the furnace design, rationally selecting the fused cast AZS block material, strictly controlling the operation parameters of the furnace, and strengthening the regular maintenance and testing measures, the erosion rate of the fused cast AZS block can be effectively slowed down, its service life can be extended, the stable operation of the glass furnace can be guaranteed, the quality and economic benefits of glass production can be improved, and the healthy development of the glass industry can be promoted. In future research and practice, it is also necessary to constantly explore new materials and technologies to further improve the corrosion resistance of glass furnace lining materials to adapt to the evolving needs of the glass industry.

Henan SNR Refractory Co., Ltd(SNR) produces a variety of high-quality fused cast AZS blocks.If you have any needs, please contact me.