
What are fused cast blocks? How are they applied in glass furnace?
The fused cast blocks, also known as “electric melting blocks”, refers to a manufacturing process of refractory bricks.
The raw materials of fused cast blocks are heated and melted in the electric arc furnace, and poured into the mold when they are in a liquid state, and then cast into specified shape after annealing and solidified.
Compared with sintered refractory bricks, the fuse cast blocks have the characteristics of compact structure, low porosity, high volume density, high mechanical strength and high temperature structural strength, and strong resistance to glass liquid erosion.
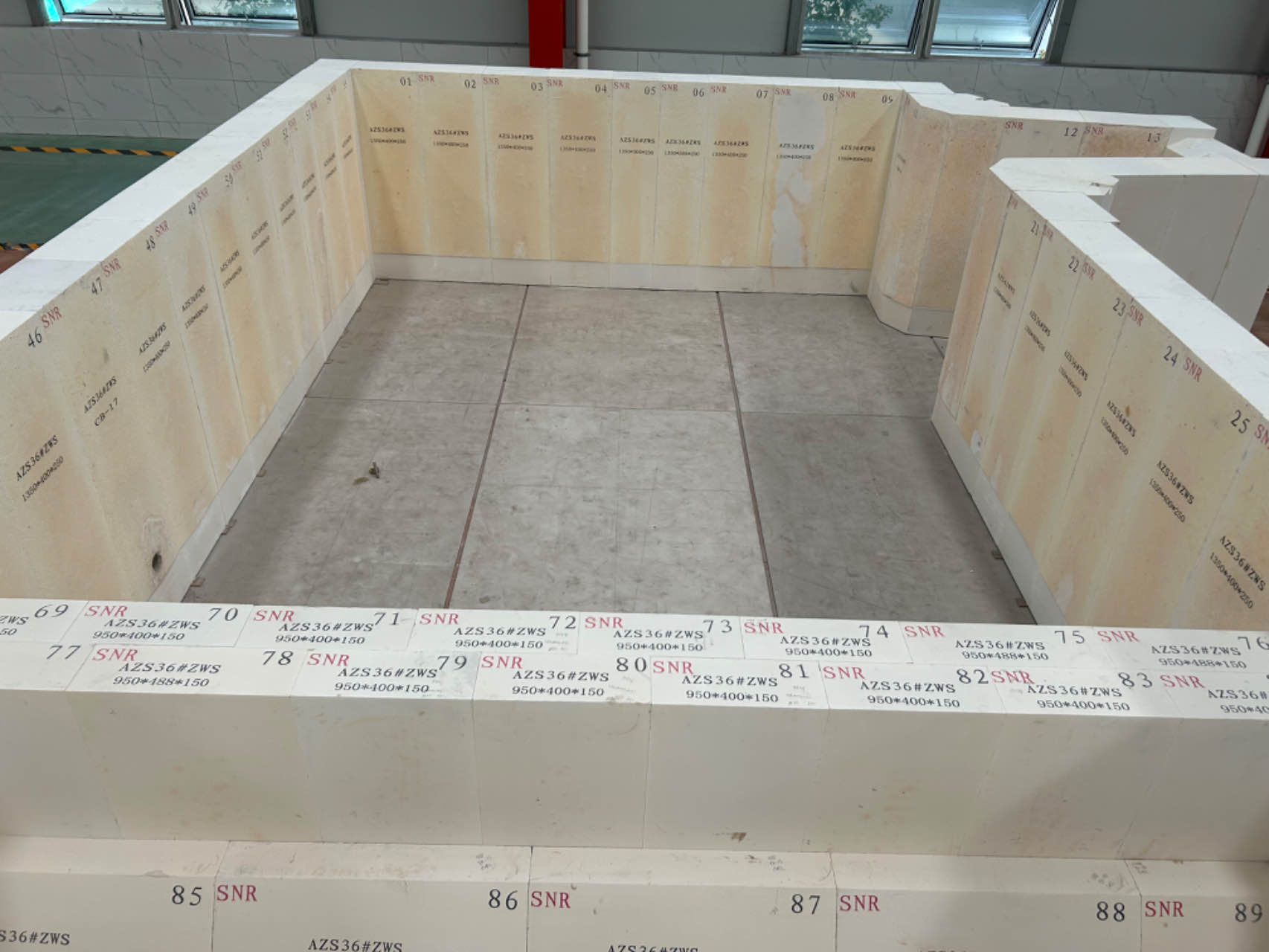

At present, the main fuse cast blocks on market are: fused mullite blocks, fused zirconia corundum blocks (fuse cast AZS), fused chromium zirconium corundum blocks, fused quartz blocks, fused corundum blocks, etc.
Which of these fused refractory materials are more suitable for use in glass melting furnaces?
1. Fused mullite brick
Fused mullite bricks use high-alumina bauxite as raw material, and different bauxites are formulated into mullite (3Al2O3·2SiO2, mass fractions are: Al2O3 72%, SiO2 28%). It is melted at about 2300°C, poured into a sand mold at 1850°C, and then annealed to relieve stress. The main crystal phases are mullite and corundum, and the glass phase is filled between the crystal phases. Its resistance to glass liquid erosion is stronger than that of sintered refractories, but not as good as other fused refractories. Adding a small amount (7% to 8.5%) of zirconia can make the mullite crystals smaller and the block structure denser, and the mullite content can be increased to 60% to 70%, which relatively reduces the content of the glass phase and reduces the cracks of the product. Fused mullite bricks are gradually replaced by fused zirconia bricks.

2. Fused zirconia corundum blocks (Fused AZS)
Fused zirconia corundum blocks are divided into three grades according to the content of ZrO2, and the corresponding grades are: AZS-33 (containing ZrO233%), AZS-36 (containing ZrO236%), AZS-41 (containing ZrO241%).

Fused zirconia corundum blocks (fused AZS) use zircon and industrial alumina as the main raw materials, and then add a small amount of zircon-rich sand (in order to increase the content of ZrO2), soda ash and borax.
According to the different atmosphere during melting, there are reduction melting method and oxidation melting method, At present, the oxidation melting method is mainly used.

The oxidation melting method can remove the pollution caused by the graphite electrode in the melt, and the carbon content is low (0.005%-0.02%), which can reduce the bubble content in the glass and improve the quality of the glass melt.
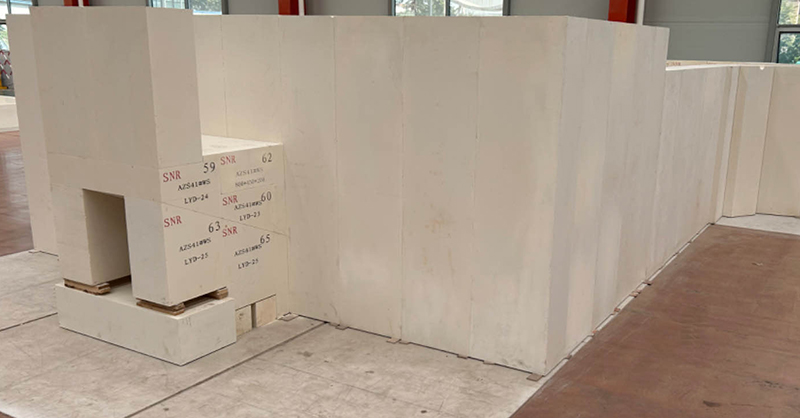

3. Fused corundum blocks
Fused corundum blocks are made of high-purity alumina as raw material, and a small amount of soda ash is added too, which is melted at 2000-2200 °C. The production process is similar to that of high aluminum products.
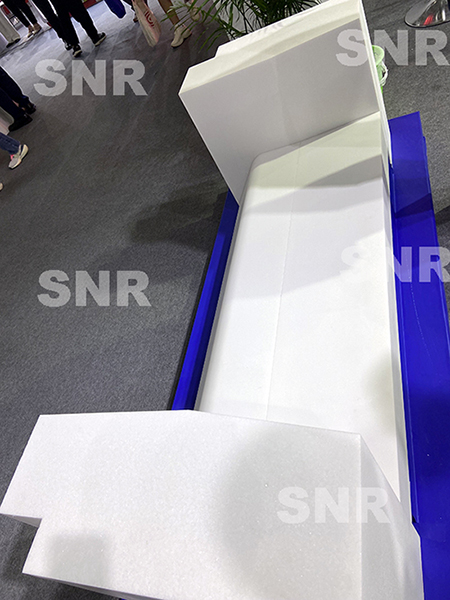

(Fuse cast corundum block lip block in working end)
There are fused α-corundum blocks, fused α, β-corundum blocks, fused β-corundum blocks, etc.
Fused α-corundum blocks are mainly suitable for melting borosilicate glass, opal glass etc. Fused α, β-corundum blocks only contain a small amount of glass phase, which will not seep out during use, less pollution to the molten glass, direct contact with the molten glass will not color the molten glass, and have good corrosion resistance. It is an ideal material for the sidewall, tank bottom of the working end furnace, and the feeder (forehearth) of the float glass melting furnace.
Fused corundum blocks are suitable for the upper structure, bottom paving of the working end, the combustion port, burner wall, working end superstructure, and burner arch etc.

4. Fused chromium zirconium corundum block
Adding 10%-30% Cr2O3 into AZS-33 blocks, and the fused chromium zirconium corundum blocks are made. (Abbreviated as AZCS blocks, French grade ER2161) by non-shrinkage casting method. The skin and interior of the blocks are dark green. The block contains 4.5% shrinkage cavity and no connected pores.
Due to the formation of aluminum-chromium spinel solid solution, the viscosity of the glass phase is increased, and the corrosion resistance of glass liquid is greatly improved. It is 3.4 times that of the fused AZS-33 block and 2.6 times that of the fused AZS-41 block.
5. Fused quartz block
The production process of fused silica blocks is the same as that of quartz glass. Use high-purity quartz sand (SiO2 content above 99.5%) as raw material, add a small amount of Na2O as a mineralizer, and melt it in a graphite resistance furnace (1750-1800°C). After melting, take out the whole piece of molten material quickly, roll it into blocks, and then machine it after cooling in the air. The thermal expansion coefficient is extremely small, and the thermal shock resistance is good. The corrosion resistance of boron glass fluid is strong, but it is not resistant to the erosion of soda lime silica glass fluid.
Fused cast refractory blocks are commonly used in the construction of glass furnaces due to their high resistance to corrosion and thermal shock. These blocks are made by melting raw materials at high temperatures and casting them into molds to form dense and durable structures.
It's important to note that the application of fused cast refractory blocks requires expertise in refractory installation, and the specific procedures may vary depending on the design and requirements of the glass furnace. Additionally, safety precautions must be taken during the installation process to protect workers from potential hazards associated with high temperatures and refractory materials.
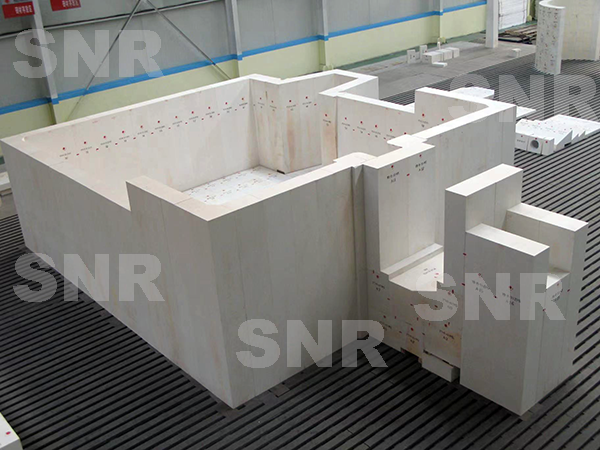

Where can you buy the high-quality fuse cast AZS blocks?
Zhengzhou SNR Refractory Co., Ltd (SNR) is a professional refractories manufacturer in China for 30 years. We export refractories to 30 countries.
Whatsapp:0086-182 0397 6036,
Email:davis@snrefractory.com.