
As an important part of modern manufacturing, the stability and efficiency of the glass industry's production process directly affect product quality and economic benefits. In the glass production process, the glass furnace is a key thermal equipment, and its operating condition plays a decisive role in the overall efficiency of the production line. As an important component in the furnace that directly contacts the high-temperature glass liquid and flame, the state of the glass furnace fused cast AZS sidewall block is directly related to the life of the furnace, the quality of glass production, and the safety of the production process. However, in the actual production process, abnormal erosion often occurs in the glass furnace sidewall blocks, which not only shortens the service life of the furnace and increases maintenance costs, but also may cause inclusions in the glass products, seriously affecting product quality.The purpose of this article is to discuss the analysis and control of the causes of abnormal erosion of sidewall blocks, which is divided into the following points:
We all know that the sidewall block plays a vital role in the glass furnace, and its importance is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
First of all, as a key component of the glass furnace, the sidewall block can directly withstand the erosion and erosion of high-temperature glass melt. The high-quality sidewall block material has high compressive strength and corrosion resistance, which can effectively protect the furnace structure from high temperature and melt damage, thus extending the service life of the furnace.
Secondly, the performance and state of sidewall blocks directly affect the quality of glass products. If the sidewall block is seriously eroded, its alteration products may enter the glass melt, forming defects such as stones and streaks, thus affecting the appearance and performance of the glass. Therefore, the selection of high-quality sidewall blocks is crucial to ensure the quality of glass products.
Then, the stability and durability of the sidewall blocks are of great significance for maintaining the overall stability of the furnace. Under high temperatures and complex chemical environments, the sidewall blocks need to maintain good dimensional stability and chemical stability to ensure the integrity and stability of the internal structure of the furnace. This helps reduce breakdowns and downtime during furnace operation and increases production efficiency.
Finally, high-quality sidewall blocks not only have excellent erosion resistance but also help optimize the operation of the furnace. For example, through reasonable design and selection of the size, shape, and material of the sidewall block, the heat distribution and flow state inside the furnace can be improved, and the uniformity and stability of the glass melt can be improved. This helps to reduce energy consumption and improve production efficiency and product quality.

The phase composition of the fused block products is clinozircon, corundum, a small amount of mullite, glass phase, and porosity. To reduce and eliminate the residual thermal stress, a certain amount of glass phase is needed in the product as an absorber to buffer the thermal stress. However, due to the existence of the glass phase, it also brings some drawbacks, as far as the corrosion resistance of refractory materials to glass liquid is concerned, the glass phase is a weak link. In the process of erosion, the glass phase is first precipitated and replaced with the high-temperature glass melt, thus accelerating the erosion of the crystal. Under the conditions of high-temperature use, the glass phase will also exude and release bubbles, which will pollute the glass melt.
General reduction method of production of fused cast AZS blocks, carburizing is more serious, according to literature reports, according to the color of the refractory section mouth to determine its corresponding carbon content: Light gray 0.03%~ 0.06%, gray < 0.03%, gray 0.08%~0.18%, dark gray 0.15%~0.19%. Even the products produced by advanced oxidation methods (long arc and oxygen blowing) contain some carbon (< 0.01%). Carburizing is in the form of carbides, nitrides, sulfides, solid carbon, and residual reducing gases. When used under oxidation conditions, gas is released, resulting in a decrease in the temperature of glass phase seepage. Fused cast AZS blocks contain more glass (fused cast AZS33 block is generally about 20%), above 1 100 ° C, will soften seepage, and with the increase of temperature and increase the loss of glass phase seepage, and the presence of carbon in the block, carbide, low-cost iron titanium and other impurities related. When there is an oxidizing atmosphere in the furnace, due to the diffusion of oxygen to the block body, it reacts with these impurities and releases gases. These gases extrude the molten glass phase, and nuclear bubbles are formed on the surface, and the crystalline phase is lost due to the loss of the combination of the glass phase, which is the reason for the erosion of the fused cast AZS blocks.
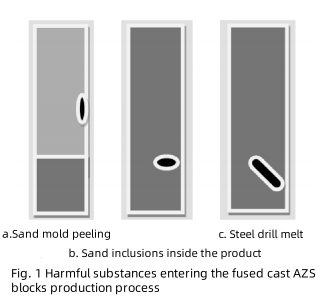
In the casting model produced by quartz sand and water glass, the sand inclusion phenomenon refers to that when the sidewall block type is poured, the high-temperature molten liquid gradually rises in the model, and the part not covered by the molten liquid passes through high temperature, and the surface sand block is separated and falls into the molten liquid, forming the sand inclusion phenomenon. As shown in Fig. 1a, the local sand skin of the quartz sand model above the molten liquid was removed from the sand mold and fell into the molten liquid due to high temperature during pouring. Fig. 1b shows the phenomenon of sand inclusion inside the product. Due to the high temperature of 1 750 ℃, the sand skin is added into the glass state inside the product. In addition, there is a flat material procedure in the melting process, the flat material tool is cast steel, steel will soften its texture in the high-temperature molten liquid for a long time, when the unmolten block is broken, the steel broken in the molten liquid may be completely melted in the molten liquid so that the iron content in the product is increased, there may be no complete melting, pouring into the product, as shown in Fig. 1c.
The oxidation degree or oxidation uniformity of fused cast AZS products is one of the key indicators of good quality. Each manufacturer has perfect system requirements in the formulation of the oxygen-blowing process, but most of them have defects in the location setting of the oxygen gun. We all know that oxygen gun hole blockage is an unavoidable phenomenon during oxygen blowing. An oxygen gun generally has 7 oxygen holes distributed around or at the bottom of the ball head, when certain or several oxygen holes are blocked, it will cause uneven oxidation degree of products, serious can be seen, not serious is not easy to intuitive judgment. Even in a single block, there will be a color inconsistency, the deep color indicates a large amount of carburizing, and the light color indicates a small amount of carburizing. The blockage of the oxygen gun hole directly leads to the poor oxidation effect of the product and the increase of the carburizing amount of the product. During the operation of the glass furnace, the glass phase is precipitated with bubbles, mostly carbon dioxide gas.
When the product is processed and ground, the flatness of the machine tool bed after aging does not meet the requirements, resulting in the product facing the middle convex or concave, and the gap is homogenized during pre-assembly, and the gap seems to be small. Due to the error of the foundation flatness or the defect of the bottom of the product, the negligence of the builder causes the bottom of the product to be raised. In the final furnace, the product expansion may not be shaped according to the homogenized gap, which may cause the bottom or upper gap of the sidewall block to increase significantly.
In the glass furnace, the improper arrangement of the weir block will also cause the deformation of the weir block due to the impact of the glass liquid. Because the weir block must withstand the impact force when the glass liquid is turned over, the weir block must have sufficient thickness and support. As shown in Fig.2 and Fig. 3 (arrows indicate the direction of liquid glass flow), the height of the supporting block needs to exceed 1/2 of the height of the weir block to be more effective. When the weir block is deformed by the impact of glass liquid, it will make the gap between the block and the block wider.


In the temperature range of the furnace, the zirconium component in the fused cast AZS block at 1100 ℃ its monocline phase into the tetragonal phase, then there will be some volume changes, temperature instability temperature reduction will occur in the opposite direction of some volume changes, this temperature fluctuation caused by the zirconium component volume reverse change is the fundamental cause of the product burst. In the furnace, an insulation stage is usually set at 1100 ° C, so that the volume of the fused cast AZS block is fully converted.
►High temperature accelerated oxidation and decarbonization: In the glass melting process, the temperature in the furnace can reach more than 1500°C. Such a high temperature environment accelerates the oxidation and decarbonization process of the sidewall blocks, resulting in structural damage of the blocks, thus accelerating the rate of erosion.
►Chemical reaction at high temperatures: At high temperatures, alkaline oxides (such as Na₂O, K₂O) and volatile components (such as fluoride) in the molten glass react chemically with the sidewall blocks to form low-melting compounds. These compounds cause the brick to be porous, weak, and easily eroded.
Chemical attack
►The influence of the composition of the compound: The soda ash, glauborite, oxide in the compound interact with the surface of the refractory at high temperature to produce a low-temperature eutectic or loose substance. These substances continue to permeate and diffuse into the interior of the block with the alternating reaction of the void or interface of the refractory itself, so that the refractory is gradually dissolved, spalling and thinning and metamorphism.
►The influence of glass composition: Some components in the glass composition, such as glauberite, fluoride, etc., will accelerate the erosion of the sidewall block. These components react with the blocck at high temperatures, resulting in changes in the block structure and a reduction in strength.
Mechanical flushing
►Washing of molten glass liquid: When molten glass liquid flows in the furnace, it has a washing effect on the sidewall block. Especially in the dynamic process of bubble rise and liquid level fluctuation, the erosion effect is more intense, which intensifies the wear and erosion of the block surface.
►Scouring of the pile: In the glass melting furnace, the flow and accumulation of the pile will also have a scouring effect on the sidewall blocks. Especially when the material pile is close to the sidewall, it will cause great erosion of the sidewall block.
Cracking caused by thermal stress
►Thermal stress caused by temperature fluctuations: Temperature fluctuations during furnace operation can cause thermal stress, resulting in cracking of sidewall blocks. The cracked brick is more vulnerable to chemical erosion and mechanical erosion, which accelerates the erosion process.
►Differences in thermal expansion and cold contraction between different materials: there are differences in the coefficient of thermal expansion and cold contraction between different materials used in the furnace, which can also lead to the acceleration of cracking and erosion of the block body.
.jpg)
Operation and maintenance factors
►Unreasonable air cooling measures: Air cooling measures are one of the important means to protect the sidewall blocks. However, if the blowing position is unreasonable, the blowing volume is too small or the blowing intensity is weak, the role of air cooling can not be fully played, resulting in accelerated erosion of the sidewall blocks.
►Influence of melting operation: Improper operation during melting operation, such as feeding speed, pile shape, etc., will affect the erosion effect of sidewall blocks. Improper operation will aggravate the erosion and erosion of the sidewall blocks.
Other factors
In addition to the above main factors, there are some other factors that will also affect the erosion rate of sidewall blocks:
►The composition and manufacturing quality of sidewall blocks: The composition and manufacturing quality of sidewall blocks directly determine their corrosion resistance. High-quality refractory materials have higher corrosion resistance and stability.
►Glass component: When the content of certain components in the glass component (such as Glauber's salt and fluoride) is high, it will accelerate the erosion of the sidewall blocks.
►Cracks and pores: Cracks and pores in sidewall blocks are channels for the penetration and diffusion of corrosive agents, accelerating the erosion process.
►The flow speed of the material pile, glass liquid, flame, and airflow: The faster the flow speed, the stronger the erosion and erosion effect on the sidewall blocks.
►Fuel combustion products and furnace atmosphere: The gases produced by fuel combustion and the atmosphere in the furnace will also affect the erosion rate of sidewall blocks.
The higher the furnace temperature, the smaller the viscosity of the glass liquid. The high temperature of the glass furnace process is required by factors, and properly increasing the glass melting temperature can improve the melting rate, reduce the viscosity of the glass liquid, and facilitate the discharge of bubbles. Reducing the viscosity of glass liquid is conducive to improving the quality of glass, but it is unfavorable to the erosion resistance of sidewall blocks, which is mainly manifested as the erosion of the crevices of sidewall block, which belongs to abnormal erosion. With low viscosity, the glass liquid is easy to enters the block joint, the glass phase of the block with the bubble precipitation, the upward movement of the bubble, and the backflow mechanical movement of the glass liquid more heavy friction erosion of the block joint, which is the root cause of the abnormal erosion of the block joint, so the smaller the block joint, the better.
When the furnace is running, the glass liquid will penetrate into the block cracks exceeding the standard. In this environment, the simultaneous upward mechanical movement of the glass liquid in the block joint with the glass phase and bubble precipitation in the block joint causes intensified erosion of the block joint. In addition, the flow of the glass liquid has a backflow effect at the gap, and this backflow effect is a mechanical flow scouring process, which will make the block joint bigger and bigger, which is one of the abnormal erosion states.
When the glass phase content of fused cast AZS block is high, inferior products will contain a large amount of impurities, the glass phase seriously exceeds the standard, and its sodium content will reach more than 2%. When the kiln is running, a large amount of glass phase will precipitate. As the glass liquid flows and the glass phase liquid rubs and moves, the glass phase precipitates a lot on one side and is taken away by the flow of glass on the other side. The erosion speed at the junction of the three phases is very fast. Some furnaces designed for 5 years will completely erode the upper 300 mm part of the sidewall in less than 2 years. This is a typical abnormal erosion phenomenon.
When the weir blocks are deformed by the impact of molten glass, the gap between the blocks will become wider. The widened gap provides space for the molten glass to exist. When the glass is accompanied by bubbles, the friction with the upward movement of the liquid glass causes abnormal erosion of the weir blocks.

(1) When there is foreign iron in the product, iron is one of the harmful substances and should be strictly controlled. Iron itself contains more than 2% carbon content, which will aggravate the erosion of products, and is also one of the harmful substances affecting the quality of glass products.
(2) There is a sand clamping phenomenon in the product, and it is concentrated.
(3) Due to the blockage of the oxygen hole of the oxygen gun, when the oxidation is not uniform, the carburizing amount of the product is high, and when the gap is encountered, the local abnormal erosion of the product is intensified due to the bubble precipitating with the glass phase.
(4) When the cross-rib cracks or localized cracks and carburization of the products converge, the reflux of the glass liquid is flushed, the glass phase content is too high and a large number of glass phases are precipitated along with the bubbles, and there is drilling erosion or even leakage of the molten glass.
Optimize refractory selection and configuration
►Select high-quality sidewall blocks: Choose reputable and reliable block manufacturers to ensure that the blocks' physical and chemical indexes and processing accuracy meet the requirements. According to the furnace's life and position, different materials and thicknesses of the sidewall blocks are selected, and the whole block code is selected as far as possible to reduce the block joints.
►Layered coding and fine processing: The upper layer is made of shallow-cast sidewall block without a shrinkage hole, and the upper and lower sidewall contact block faces are finely processed to ensure that the block seam is small.The lower layer is made of corrosion-resistant materials such as fused cast AZS blocks to improve fire resistance.
Improve construction quality and furnace design
►Ensure construction quality: The construction quality is ensured when the sidewall block is constructed, the size of the block joint meets the requirements, and the upper and lower contact surfaces are tight, so as not to damage the block body. Before ignition, the expansion joint around the sidewall should be checked and cleaned to ensure the structural integrity of the furnace.
►Design a scientific and reasonable temperature rise curve: Design a scientific and reasonable heating curve to ensure the quality of the furnace. In the temperature range where the expansion of the fused cast AZS block changes greatly (such as 1000~1100℃), an insulation process is designed to reduce the impact of the furnace on the sidewall blocks when the furnace passes the fire.
Optimize furnace operation and maintenance
►Proper use of cooling air system: According to the running time of the furnace and the erosion of the sidewall, the cooling air volume is adjusted in stages. In the design, the cooling air of the sidewall in the melting zone is divided into two sections, and different cooling fans are set to cool the sidewall. Adjust the position of the air nozzle in time, reduce the temperature at the three-phase interface, and reduce the erosion speed.
►Stabilize the liquid flow in the furnace: Improve the melting operation capacity, and avoid large changes in the pile position, partial material, and liquid level ups and downs. Optimize the flow hole and platinum pipe design to eliminate eddy currents and reduce scour on refractories.
►Optimized feeding method: Optimize the feeding equipment to reduce the size and frequency of the fluctuation caused by the feeding. The feeding point is extended, the pile area is reduced, and the glass liquid level in the furnace is stabilized.
►Regular cleaning and inspection: Clean the inside of the furnace regularly to remove sediment attached to the wall tiles and reduce chemical erosion. Conduct a thorough inspection of sidewall blocks, record erosion, and promptly identify and deal with potential problems.

Take emergency and preventive measures
►Rapid cooling and isolation: Once signs of cracking of sidewall blocks are found, the fuel supply of the furnace should be adjusted immediately to reduce the temperature in the furnace and slow down the rate of erosion. Use refractory materials to temporarily seal the burst area to prevent the leakage of molten glass.
►Partial replacement and repair: After the furnace is cooled to a safe range, the personnel are quickly organized to clean up the damaged area and replace the new sidewalls. The sidewall area with light erosion can be treated by local repair.
►Preventive replacement program: According to the operation records of the furnace and the erosion rules of the sidewalls, make a preventive replacement plan to replace the sidewalls that are about to reach their service life in advance.
Enhanced protective layer: After replacement, the sidewall surface is coated with a layer of high-temperature and corrosion-resistant protective paint or coating to improve its corrosion resistance.
Optimize the energy distribution of the furnace
►Adjust the fuel and electric fusing power ratio: In the later stage of furnace operation, optimize the energy distribution of the furnace, increase the proportion of energy provided by gas, and reduce the proportion of electric energy. Reduce the electric melting power, reduce the surface temperature of the electrode block, and slow the erosion rate of the electrode block and sidewall block.
►Focus on furnace process changes: During the optimization of the furnace energy ratio, we should always pay attention to the changes in the furnace process and production. Minimize the adjustment amplitude and frequency to avoid the decline of product output and quality caused by process adjustment.
Through the in-depth analysis of the reasons for the abnormal erosion of glass furnace sidewall blocks, we can recognize that this phenomenon is the result of the comprehensive action of many factors. High-temperature environment, chemical erosion, mechanical erosion, thermal stress, as well as the composition of sidewall blocks, manufacturing quality, glass composition, cracks and pores, flow speed, fuel combustion products furnace atmosphere, etc., are all causes that can not be ignored.
To effectively control the abnormal erosion of the glass furnace sidewall, we must take comprehensive measures. This includes optimizing furnace operating parameters to reduce the erosion of sidewall blocks by adverse factors; Use high-quality refractory materials to improve the corrosion resistance of sidewall blocks; Improve the masonry technology to ensure the masonry quality of sidewall blocks; Strengthen daily maintenance and hot repair, timely detection and treatment of erosion problems; And reasonable use of cooling air system.
On this basis, we especially recommend SNR fused cast AZS block as the preferred material for glass furnace sidewall blocks. Because of its excellent high-temperature stability, corrosion resistance, and durability, SNR fused cast AZS block has a wide range of applications in the field of glass production and a good reputation. Its unique manufacturing process and advanced material formulation make SNR fused cast AZS block can maintain stable performance under extremely high-temperature environments, and effectively resist the erosion of molten glass and its components, thereby extending the service life of the furnace and improving the quality and efficiency of glass production.

Therefore, for the pursuit of high quality, high efficiency, and low-cost glass production enterprises, the choice of SNR fused cast AZS block as the material of furnace sidewall block is undoubtedly a wise and economic decision. We believe that in the future development, SNR fused cast AZS block will continue to contribute more to the sustainable development of glass production enterprises with its excellent performance and reliable quality.
If you have any needs for refractory materials, please contact us.
 Email:moon@snrefractory.com Web:www.snrefractory.com
Email:moon@snrefractory.com Web:www.snrefractory.com